What are the amplifier circuits of the triode?
Since the input impedance of the common-emitter amplifying circuit is high, it is possible to directly connect the signal source to be amplified, and then use the "Walmanization" of the common-base amplifying circuit to eliminate the "Miller effect", increase the bandwidth, and finally connect the load through the common-amplifier circuit. Because the output impedance of the common amplifying circuit is low, it acts as a buffer and can drive heavy loads.
1, a common amplifier circuit
The circuit schematic is as follows:
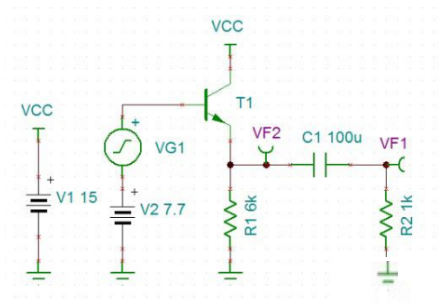
1. The magnification is: A=1. When the output voltage is applied, the input voltage is subtracted from the transistor voltage drop of the transistor by 0.7V.
2. Output impedance: Zout = Re / beta. Also due to the circuit amplification characteristics of the triode, the Re conversion to the output needs to be reduced by a factor of beta, so the output impedance is low. (This is also the most important advantage of the common amplifier circuit) .
3. Input impedance: Zin = beta * Re. Due to the circuit amplification characteristics of the three-stage tube, the Re conversion to the input needs to be amplified by a factor of beta, so the input impedance is high.
4. Frequency characteristics: The common-amplifier circuit does not have the Miller effect, so the frequency characteristics are very good.
2, common emission amplifier circuit
The circuit schematic is as follows:
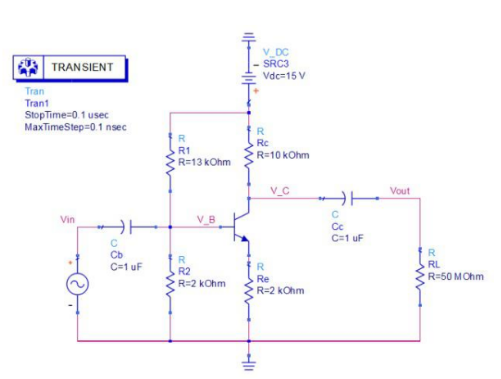
1. Input impedance: Zin = beta * Re. (R1 and R2 provide the bias voltage for the triode, which is ignored here, of course, should be considered.) Due to the circuit amplification characteristics of the three-stage tube, the Re conversion to the input needs to be amplified by a factor of beta, so the input impedance is high.
2. Output impedance: Zout = Rc. In order to reduce the current of the three-stage tube and reduce the power consumption, Rc generally takes a large value.
3. The magnification is: A=-Rc/Re. Design the values of Rc and Re according to needs.
4. Frequency characteristics: Due to the Miller effect, the parasitic capacitance between the base and collector of the triode will increase the A-fold response to the input end in the amplification region, so the frequency characteristics are poor and the high-frequency signal cannot be amplified.
3, common base amplifier circuit
The circuit schematic is as follows:
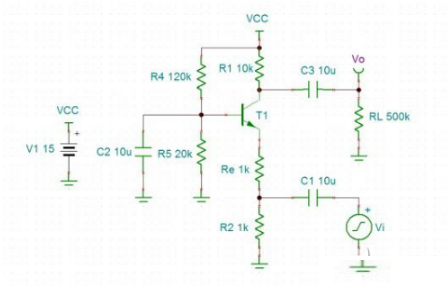
1. Input impedance: Zin = Re. (Also ignore the bias voltage of the base). Due to the lack of "isolation" of beta amplification, the input impedance is not large, which is a disadvantage.
2. Output impedance: Zout = Rc. The output impedance is the same as the common-emitter amplifier circuit, which is also a disadvantage.
3. The magnification is: A=Rc/Re. The amplification principle is the same as the common-emitter amplifier circuit. However, for forward amplification, the common-emitter amplifier circuit is reverse-amplified.
4. Frequency characteristics: The base of the common-base amplifier circuit has a large capacitance and is an AC base, so there is no Miller effect and the frequency characteristics are good.
Other amplifying circuits are based on the deformation of the first three kinds of amplifying circuits. As long as the above three kinds of amplifying circuits are deeply understood, others can be quickly grasped. The differential amplifying circuit reduces the influence of the common-emitter amplifying circuit. The power amplifier and the rear stage amplifying circuit in the sound are the deformation of the common amplifying circuit. A good power amplifier will be more complicated than the Class A, Class B, and Class A power amplifiers, but the principle is still similar.
If you want to know more, our website has product specifications for the triode, you can go to ALLICDATA ELECTRONICS LIMITED to get more information

