What is the difference between triode and MOS control?
Why do you often see that when you use the single-chip I / O port to drive the MOS tube, you do n’t use the single-chip I / O port to directly drive, but instead use the triode to drive the MOS tube through the first-level transistor.
Transistor and MOS tube control difference
Transistors and MOS transistors are different in driving. Transistors are current-driven, while MOS transistors are voltage-driven. As long as the base driving voltage of the triode is higher than the dead zone voltage of Ube, the triode can be turned on. The voltage of the zone is generally 0.6V, and the dead zone voltage of the germanium material transistor is generally 0.3V, so the voltage of the control transistor is only higher than about 0.6V for the silicon material triode, and only high for the germanium material triode It can be around 0.3V.
The MOS tube is different. The MOS tube is a voltage-driven. The driving voltage must be higher than the minimum value of the dead zone voltage Ugs to be turned on. The minimum Ugs of different types of MOS tubes is different, generally It is about 3V ~ 5V, the smallest one is 2.5V, but it is just turned on, its current is very small, and it is still in the initial stage of the amplification area. Generally, the driving voltage when the MOS tube reaches saturation is about 6V ~ 10V.
Practical application
After understanding the difference between the transistor and the MOS tube in control, how can the microcontroller I / O port control the transistor and MOS tube? The single chip microcomputer generally uses 5V or 3.3V power supply, and its I / O port high level is 5V or 3.3V. The processor generally pays attention to low power consumption. Nowadays, there are many single chip microcomputers using 3.3V power supply, so its I / O port high level Only 3.3V.
(1) The voltage of 3.3V is enough to drive the transistor. The transistor is a current drive. The base current can be calculated according to the voltage VIO of the I / O port and the value of the current limiting resistor R1, Ib = (VIO-0.6V) / R1, You can change the base current by choosing a different resistance R1. As long as VIO is greater than 0.6V, you can make the transistor work in the saturation region. The following figure shows the principle of a simple NPN transistor to control the LED indicator.
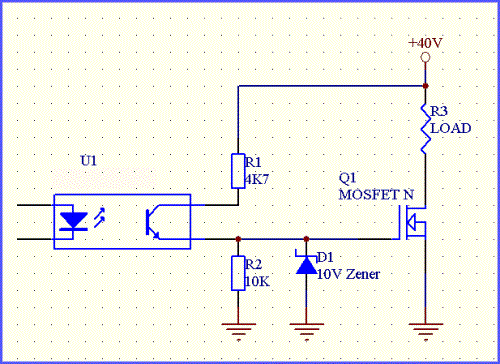
(2) The MOS tube is driven by voltage. The minimum drive voltage of the MOS tube is about 3V ~ 5V. The drive voltage of different types of MOS tubes is different. The minimum drive voltage of some small power MOS tubes is about 2.5V. The single chip I / O port can be directly driven However, at this time, the MOS tube is in a semi-conducting state, and the internal resistance is large, so it can be used to drive a small current load. Large current loads can not be used in this way, the internal resistance is large, the power consumption of the tube is too large, and it is easy to burn the MOS tube. The driving voltage required for the MOS tube to reach the saturation state is generally about 6V ~ 10V, and the voltage of 3.3V is not enough to directly drive the MOS tube to saturate it. Therefore, you can add a transistor in the output end of the I / O port to make the driving voltage of the MOS tube higher. For example, for reference only, the principle is shown in the figure below.
Principle analysis: when the I / O port of the single-chip microcomputer is high, the NPN transistor Q5 is turned on, and the control pole of the N-MOS tube is directly pulled down, the MOS tube is cut off, and the load does not work; when the I / O port of the single-chip microcomputer is low Normally, the NPN transistor Q5 is cut off, and the resistors R12 and R13 divide the 24V power supply so that the G pole voltage is: 24V * 20K / (10K + 20K) = 8V, the MOS tube turns on and reaches saturation, and the load works.
Summary: The transistor is driven by current, the lower voltage can drive the transistor, and the MOS tube is driven by voltage, the driving voltage is higher, the voltage of the single-chip I / O port is not enough to drive the MOS tube, so the transistor is often used as a buffer to change the voltage Of course, in addition to using transistors, optocouplers can also be used.
If you want to know more, our website has product specifications for triode and MOS control, you can go to ALLICDATA ELECTRONICS LIMITED to get more information

