What are the methods for preventing the reverse connection of the MOS tube?
Reversely connect the power supply, which will cause damage to the circuit. However, reversely connecting the power supply is inevitable. Therefore, we need to add a protection circuitto the circuit. The protection circuit can achieve the purpose of not damaging even if the power supply is reversely connected.
Generally, a diode can be connected in the positive pole of the power supply. However, because the diode has a voltage drop, it will cause unnecessary loss to the circuit, especially in battery-powered applications, the original battery voltage is 3.7V, the diode will reduce the voltage by 0.6V, and the battery life will be greatly reduced.
MOS tube anti-reverse connection, the advantage is that the pressure drop is small, small enough to be negligible. The current MOS tube can achieve several milliohms of internal resistance. Assuming a 6.5 milliohm MOS transistor with a current of 1A, the voltage drop is only 6.5 millivolts.
Because MOS tubes are getting cheaper and cheaper, there are more and more people using MOS tubes to prevent reverse power connections.
NMOS tube prevents power reverse circuit:
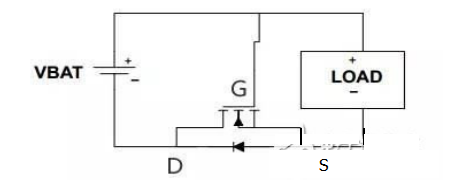
When connected correctly: just after power-on, the parasitic diode of the MOS tube is turned on, so the potential of S is about 0.6V, and the potential of G is VBAT, VBAT-0.6V is greater than the threshold voltage of UGS, DS of MOS tube Will be turned on. Since the internal resistance is small, the parasitic diode is short-circuited and the voltage drop is almost zero.
When the power supply is reversed: UGS=0, the MOS tube will not be turned on, and the circuit of the load is broken, thus ensuring circuit safety.
PMOS tube prevents power reverse circuit:
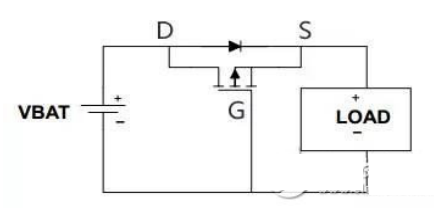
When properly connected: just after power-on, the parasitic diode of the MOS transistor is turned on, and the power supply and the load form a loop, so the S pole potential is VBAT-0.6V, and the G pole potential is 0V, the PMOS transistor is turned on, and the current flowing from D to S Causes a short circuit in the diode.
When the power supply is reversed: the G pole is at a high level, and the PMOS tube cannot be turned on, so the circuit can be protected.
Connection skills
The NMOS transistor DS is connected to the negative pole, and the PMOS transistor DS is connected to the positive pole, so that the parasitic diode direction is toward the direction of the current of the correct connection.
Feeling that DS flow direction is "reverse"?
Careful friends will find that the current flow of DS in the anti-reverse circuit is opposite to the current direction we usually use.
Why do you want to reversely connect?
Utilizing the conduction of the parasitic diode, UGS meets the threshold requirement just after power-on.

