What factors should be considered in the PCB design process of GTP signals for FPGAs
Gigabit serial I/O technology has excellent performance, but these superior performance are guaranteed by conditions that are excellent signal integrity. To improve the success rate of high-speed, gigabit serial designs for specific applications, we may need to simulate and use a new, more complex bypass circuit.
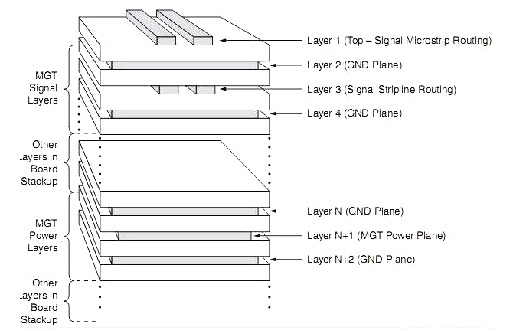
The GTP performance of Spartan-6 FPGA depends on the signal integrity of the PCB. The following factors must be considered in the PCB design process: the stack structure of the board, the layout of the components, and the signal routing.
l Power supply and stack
For the GTP transceiver of the Spartan-6 FPGA, the stack can be divided into two groups, a power distribution layer and a signal trace layer. The power plane is used to connect GTP's MGTACC, MGTAVCCPLL, MGTAVTTTX and MGTATVTTR power pins.
The power plane of the GTP should be closely adjacent to the ground plane to increase the coupling effect. The ground plane can provide shielding for the GTP power plane, and the shield power plane is caused by noise interference caused by the signal of the upper layer or the next layer.
In fact, from another point of view, when the noise of the power supply appears in the high frequency range, as the frequency increases, it becomes more and more difficult to find a capacitor that can cover this frequency range, and the filtering effect is achieved until it is impossible to find such a capacitor. . As the capacitance value decreases, the associated stray inductance and the resistance value of the package do not change accordingly, so the frequency response does not change too much. In order to achieve better power distribution at high speeds, we need to use the power plane and ground plane to build our own capacitors. In order to achieve our goals more effectively, it is often necessary to use adjacent power and ground layers.
The connection between the GTP's power pins and the power distribution network plays a key role in the performance of the GTP. PDN, and FPGAs require low impedance and low noise connections. The GTP power supply of the FPGA tolerates a maximum noise of 10mVpp. In the range of 10KHz to 80MHz, the power supply can use a small plane. This small power plane should not cover the area of the SelectIO interface.
l Capacitor placement
In addition to considering the value of the bypass capacitor, another important aspect to consider is the placement of the capacitor.
The general rule is that the larger the capacitance value, the less stringent the placement requirements. If the capacitance is small, the capacitor should be as close as possible to the power and ground pins. One method that can be used is to remove unused common IO traces and vias to make room for bypass capacitors.
l Signal trace
GTP signal traces and SelecTIO signal traces should be avoided in adjacent layers, and their respective return paths should remain separated, including vias.
It is important to maintain a certain distance between differential pairs and between differential and other lines. The usual rule is that the distance between adjacent pairs of lines is at least 5 times greater than the line.
Gigabit-level signal differential lines should avoid changing the trace layer as much as possible. If cross-layer transmission is a must, then special care is required. First, you must provide a complete return path. So we have to couple the reference layer of layer A with the reference layer of layer B. Ideally, both reference layers are formations. In this case, the return path can be achieved by placing another via connecting the two reference layers near the transfer via.
If the reference layers are different (one is the ground plane and the other is the power plane), you need to place a 0.01μF capacitor as close as possible to the vias to connect the two reference layers, reducing the impedance of the return path.

