What is the principle of 2.4G wireless transceiver module?
2.4G is a wireless technology, because its frequency band is between 2.400GHz and 2.4835GHz, referred to as 2.4G wireless technology. The highly integrated chipset based on 2.4G wireless technology package is called 2.4G wireless module, and 2.4g wireless transceiver module is one of the numerous 2.4G wireless modules, widely used in wireless remote control, wireless headset, drone, Wireless keyboards, wireless monitoring, contactless RF smart cards, small wireless data terminals, security fire protection systems, wireless remote control systems, biosignal acquisition, hydrometeorological monitoring and other industries and commodities.
The wireless transmit and receive modules have been packaged (integrated with single-chip control and wireless coding) and directly connected to the single-chip microcomputer through the asynchronous serial port. Now the wireless transceiver module on the market, its wireless working mode is controlled by the single-chip microcomputer inside the module. The connection with the user's single-chip microcomputer generally only has several lines such as power supply, receiving and transmitting.
The wireless transmitting module and the receiving module must be paired and used, and the working frequency must be exactly the same. The receiving module must match the decoding IC according to the local encoding format of the transmitting. The wireless transceiver module is a channel for transmitting data, and the receiving module receives the transmitting signal. Pass the DA TA foot to the decoding IC and let it work.
2.4g wireless transceiver module principle
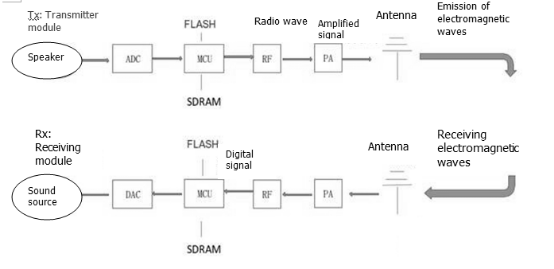
What is the working principle of the 2.4G wireless transceiver module? The purpose of wireless transmission is to free yourself and replace wired connections with wireless technology. How to replace? Simply speaking, the 2.4G wireless transmission transmits electromagnetic waves through the receiving module receiving the sound source processing, and the receiving module receives the electromagnetic waves radiated into the air by the transmitting module, and transmits them to the horn through digital-to-analog conversion.
Microphone wireless transceiver module structure function
ADC/DAC: Analog to Digital Converter / Digital to Analog Converter
MCU: Single-chip microcomputer (equivalent to computer CPU)
FLASH: memory chip (equivalent to computer hard disk)
SDRAM: Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory (equivalent to computer memory)
RF: Wireless RF
PA: Power amplifier
As shown in the above figure, the transmitting module collects the sound source and converts the analog signal into a digital signal through analog-to-digital conversion. After the MCU code runs and processes the central processor (the MCU can integrate the peripheral interfaces such as converter, power supply, USB, memory, etc.) On a chip) RF signals are radiated into the air to form electrical waves. In order to obtain a longer transmission distance, the electromagnetic electromagnetic wave signal can be amplified by the PA and finally transmitted through the antenna. The receiving module antenna is connected to the electromagnetic wave emitted by the transmitting module, and is converted into a digital signal by RF amplification signal through the PA, and is also processed by the MCU and finally converted into an analog signal by digital mode to transmit the sound through the speaker. A complete wireless transmission principle is probably the case. Of course, whether the transmitter module or the receiver module is powered by a power supply, the 3.5Lline in interface can be used for the module audio source.

