How to judge the positive and negative of the primary battery?
Primary battery working principle
The primary battery reaction is an exothermic reaction, generally a redox reaction, but unlike the general redox reaction, electron transfer is not accomplished by an effective collision between the oxidant and the reducing agent, but the reducing agent is lost on the negative electrode. The electron undergoes an oxidation reaction, and electrons are transported to the positive electrode through an external circuit, and the oxidant undergoes an electron reduction reaction on the positive electrode to complete electron transfer between the reducing agent and the oxidant. The directional movement of ions in the solution between the two poles and the directional movement of electrons in the external conductor constitute a closed loop, so that the two electrodes react continuously, an ordered electron transfer process occurs, and a current is generated to convert the chemical energy into electrical energy.
However, it should be noted that the non-redox reaction can be designed as a primary battery. From the perspective of energy conversion, the primary battery is a device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy. From the perspective of chemical reaction, the principle of the primary battery is that the electrons lost by the reducing agent in the redox reaction are transferred to the oxidant via the external wire to make the redox reaction. Performed on two electrodes separately.
The conditions that make up the primary battery
(1) the electrode materials are all inserted into the electrolyte solution;
(2) The two poles are connected to form a closed circuit;
(3) There are two kinds of metals (or one type of non-metal element or metal oxide) which are different in activity;
(4) Internal conditions: The redox reaction can be spontaneously carried out.
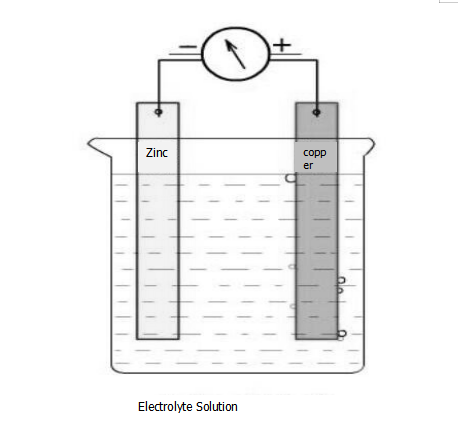
As shown above, the primary battery consists of:
(1) When the electrolyte solution is a CuSO4 solution: the Zn electrode is a negative electrode, the electrode reaction is Zn-2e- = Zn2+, the reaction is an oxidation reaction; the Cu electrode is a positive electrode, and the electrode reaction is Cu2+ + 2e- = Cu, The reaction is a reduction reaction.
(2) When the electrolyte solution is dilute H2SO4: the Zn electrode is a negative electrode, the electrode reaction is Zn-2e- = Zn2+, the reaction is an oxidation reaction; the Cu electrode is a positive electrode, and the electrode reaction is 2H+ + 2e- = H2 ↑, This reaction is a reduction reaction.
Judging the positive and negative of the primary battery
1. Judging by whether or not the electrode material is dissolved. The negative electrode of the primary battery may be dissolved, and the positive electrode must not be dissolved; on the contrary, the electrode that gains weight or has bubbles is positive.

