What are the applications of Hall current sensors in telecommunications rectifiers?
Both the power factor correction (PFC) circuit and the inverter circuit in the telecommunication rectifier and server power supply unit (PSU) need to detect the current signal on the high voltage side to the controller on the low voltage side, so an isolated current sensor is used. There are multiple implementations of isolated current detection, such as current transformers (CT), isolation amplifiers, and Hall-effect current sensors. Among them, the Hall effect current sensor is an ideal choice because it is simple, easy to use, accurate, small in size and has DC detection capability.
The current transformer is based on the principle of the transformer to sample the current. Using CT can detect the turn-on current of the MOSFET or IGBT. The fast response speed of CT makes it very suitable for peak current control and overcurrent protection control. However, CT based on the principle of transformer coupling cannot sense DC or very low-frequency currents, resulting in its inability to directly detect power-frequency AC currents, or loss of measurement accuracy due to indirect methods that only detect turn-on current (no turn-off current). In addition, because the CT needs to use a ferrite core, the volume is difficult to make small, and the larger CT will increase the power switching loop, resulting in higher voltage spikes and noise interference.
The Hall effect current sensor is a more accurate and smaller choice. It can work under DC conditions, and can measure the total AC current including turn-on and turn-off with good linearity and accuracy. At the same time, the volume of the Hall-effect current sensor can be packaged in SOIC-8, the same size as an integrated IC, making PCB layout easier and helping to achieve higher power density.
When applying Hall-effect current sensors to telecommunications power supplies or server PSUs, it is necessary to evaluate the current detection range, continuous current tolerance, response speed (/ bandwidth), and voltage isolation level. In some cases, the telecommunications power supply or server power supply may also need to report the current operating power to the host computer. At this time, a high-precision Hall current sensor (such as TI's TMCS1100) can help the system achieve ≥1% current detection accuracy.
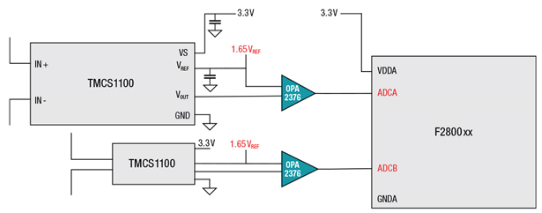
Typical application circuit of Hall-effect current sensor when using 3.3 V and 5 V power supply respectively. Compared with using 3.3 V power supply, using 5 V power supply can widen the current detection range of the Hall sensor. Taking TMCS1100A1 as an example, the sensitivity of the Hall sensor is 50 mV / A: if a 3.3V power supply is used, the current detection range is -33 A to + 33 A (bidirectional); while using a 5.0V power supply, the current detection range can be extended To -50 A ~ + 50A. In addition, it should be noted in the design that in addition to the current detection range, the continuous current withstand capability of the sensor also needs to be considered. When the current withstand capability is insufficient, it can be optimized by improving the heat dissipation of the sensor.
In the circuit board layout using Hall effect current sensors, pay attention to the following factors:
Heat dissipation: increase the copper area of the primary current conductor as much as possible to improve the heat dissipation capacity of the Hall current sensor, thereby increasing the maximum average current tolerance of the sensor. In addition, you can use a thicker copper foil PCB, or place some heat dissipation vias on the primary trace, or place the Hall current sensor and PCB trace in the air duct, which can improve the average current resistance of the Hall current sensor. Subject to ability.
Primary current magnetic field: When laying out, you should try to avoid large current traces close to the Hall current sensor. Isolation requirements: Consider the creepage distance and electrical clearance from the overall system. When the Hall current sensor cannot meet the required PCB creepage distance, you can dig grooves on the circuit board to achieve system-level isolation requirements. In telecommunication rectifiers and server PSUs, CT is more suitable for peak current control and overcurrent protection, but it is larger and less accurate. The Hall effect current sensor is small in size, high in accuracy, simple and convenient to use, and more suitable for detecting AC line current.
If you want to know more, our website has product specifications for rectifiers, you can go to ALLICDATA ELECTRONICS LIMITED to get more information

