What is going on with inductor saturation?
The term “inductance saturation” is so unfamiliar—I don’t know what it means, except for the appearance of current bending and distortion, and burned out devices. What does “saturation” actually mean in physical terms?
Inductance, temperature resistance, saturation current, size, and price, these five are the basic coordinate systems for our inductor selection. Of course, we will also consider the shape of coils and cores, magnetic materials, and installation and welding methods. The most annoying in the selection process is to find a suitable one among dozens of inductors, but found that one of the parameters does not meet the requirements, or the saturation current caused by the peak power with extremely low probability of occurrence is too large. Design margin.
Sensual secret
The reason why the inductor is inductive, that is, the current flowing through the inductor lags the current applied to the inductor (in fact, it lags the phase angle of 90 degrees), because of Lenz's law, the inductor is like a bear catching a pet at home and obstructing For the pet's progress (the change of current), you have to put some pressure on the bear child, he will be reluctant first, and then let the pet (current) walk (we make full use of this disobedient feature to achieve our choke choke Purpose); inductance is like a spring. When you apply pressure, it stores part of the energy in its body and transmits the remaining part of the energy. When the spring is compressed to the extreme, it cannot store more energy. That is, saturation occurs, all the increased energy is transferred out, and the inductance loses its hysteresis.
In terms of physics, the example of spring may be more appropriate, like the following textbook-like answer I found on the Internet:
The electrons revolve around several layers of orbits in the outer layer of the atom. Each layer of electron rotation will generate a weak magnetic field according to the law of stupefaction. The magnetic force and direction of each layer are different, but the combined force is zero and there is no magnetism. When a coil is energized, a magnetic field is generated in the same way according to the law of stupefaction. The lines of magnetic force pass through the magnetic material (iron core), and the electron orbits of atoms in the magnetic material begin to turn to offset the lines of magnetic force generated by the coil. The larger the coil current, the more When the direction of rotation of the electrons of the magnetic material changes, and the direction of the electrons of all magnetic materials is the same, it is magnetic saturation.
Reasons and theoretical analysis of inductance magnetic saturation
When we superimpose a common direction of rotation on all electrons, just like a uniform army phalanx, its magnetic force is reached, and the magnetic force cannot be increased and it becomes saturated.
This kind of explanation is vivid enough to qualitatively explain the concept of saturation, but qualitativeness does not satisfy me. The charm of physics is far more than qualitative analysis.
The physical meaning of inductance saturation
When we talk about inductor saturation, we are actually talking about iron core saturation—a hollow inductor will never be saturated. At this time, the intuitive question is: why not use hollow inductors?
This must start from the calculation formula of the inductance: (Here, draw the conclusion directly, the specific derivation will be mentioned in the next part)
Where is the inductance, magnetic permeability, the equivalent number of turns of the winding, the equivalent cross-sectional area of the magnetic circuit, and the equivalent magnetic circuit length of the inductance coil.
Obviously, to increase the inductive value, you can increase the numerator and decrease the denominator. Often limited by volume (especially the power inductor’s wire is very thick, each turn will greatly increase the volume, and the increase will also increase), wire resistance (heating), parasitic capacitance (especially EMC inductance, parasitic capacitance will greatly weaken it High frequency suppression capability). Under the same dimensions, improvement is almost the way. The permeability of air is almost equal to the permeability in vacuum, and magnetic materials with excellent performance can be reached. Compared with the inductance with magnetic core, the inductance of air-core inductors will be thousands of times different.
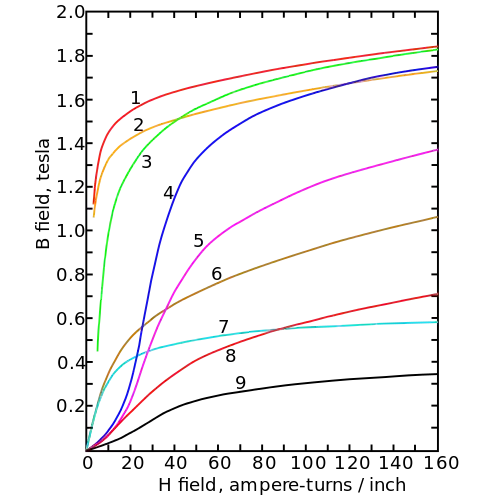
Nine kinds of ferromagnetic materials represent the magnetization curve of magnetic saturation.
1. Steel plate,
2. Silicon plate,
3. Steel casting,
4. Tungsten steel,
5. Magnetic steel,
6. Cast iron,
7. Nickel,
8. Cobalt,
9. Magnetite
It helps us gain high value, but it also brings us the problem of saturation. The relationship between magnetic field intensity and magnetic induction intensity can be expressed by permeability: the permeability of a magnetic material is not a constant quantity, but depends on
the magnetic field intensity. In the metal that will be magnetically saturated, as the current through the inductor increases, the relative permeability reaches a value with the increase of the magnetic field strength, and then as its saturation decreases, it will become 1, so the corresponding inductance also tends to The hollow inductor, in other words, becomes a wire, which is the physical meaning of inductor saturation.
The inductance will not disappear, it will only degenerate into an air core inductance.
Curve (in many textbooks it has another name: hysteresis loop, of course, there are three other quadrants of hysteresis loop) as shown in the figure below, at the right limit of the curve, all materials will tend to the same straight line , This is the physical convergence of nature:
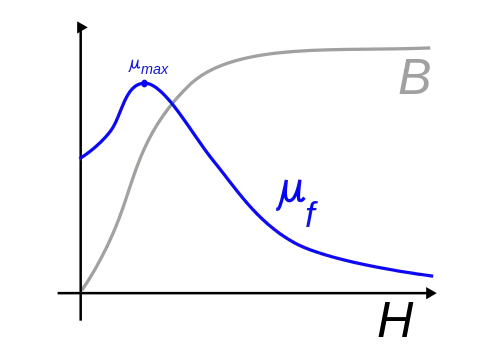
Because of magnetic saturation, the magnetic permeability μf of ferromagnetic materials will increase to a value with the increase of the magnetic field strength, and then gradually decrease.
Calculate everything with Maxwell's equations!
All electromagnetic-related physical quantities can be derived from Maxwell's equations. Inductance is no exception.
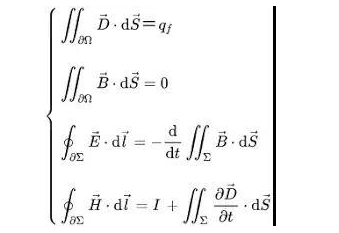
The physical definition of inductance (only self-inductance is considered here) is It describes the ability to generate back-induced electromotive force at a unit current rate of change.
One of the most disturbing facts in physics is that the definition is often not a formula for design. For the latter, we will have a more commonly used calculation formula. Let’s derive it below:
According to Faraday’s law (one of Maxwell’s equations), the induced electromotive force is equal to the rate of change of magnetic flux (), If it is a multi-turn coil, you also need to consider the equivalent number of turns of the winding.
This article is from Allicdata Electronics Limited which offer electronic components, semiconductors, antennas, capacitors, connectors, diodes, transistors, IC,resistors. For more product information, please go to the website to get it.

